----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*** SPECIAL NOTE FROM DR. WICHMAN ***
The following excellent article was reproduced from Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3899137/:
Tolerogenic vaccines for Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
Tolerogenic vaccines represent a new class of vaccine designed to re-establish immunological tolerance, restore immune homeostasis, and thereby reverse autoimmune disease. Tolerogenic vaccines induce long-term, antigen-specific, inhibitory memory that blocks pathogenic T cell responses via loss of effector T cells and gain of regulatory T cell function. Substantial advances have been realized in the generation of tolerogenic vaccines that inhibit experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in a preclinical setting, and these vaccines may be a prequel of the tolerogenic vaccines that may have therapeutic benefit in Multiple Sclerosis. The purpose here is to provide a snapshot of the current concepts and future prospects of tolerogenic vaccination for Multiple Sclerosis, along with the central challenges to clinical application.
Immunogenic and Tolerogenic Vaccines: A Primer
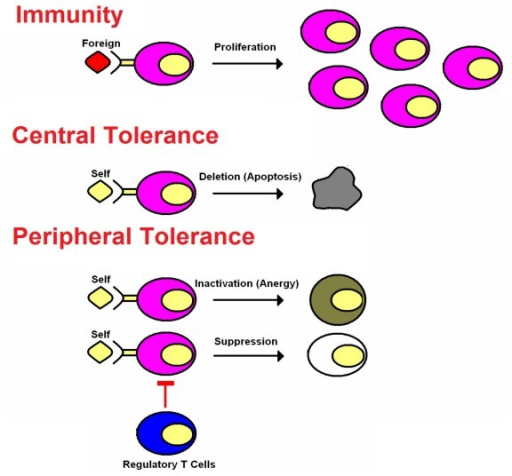
The classic immunogenic vaccines represent one of the most successful and cost-effective interventions in the history of medicine. The field of vaccination is now rapidly expanding to encompass a new class of vaccines (i.e., the tolerogenic vaccines) that induce immunological tolerance to alleviate the inflammatory autoimmune diseases as well as other inflammatory diseases of metabolism, neurodegeneration, allergic hypersensitivity, and transplantation rejection. Immunogenic and tolerogenic vaccines differ in many fundamentals. First, immunogenic vaccines have had unparalleled clinical success, including the elimination of smallpox and the near-eradication of polio and are credited with saving untold millions of lives. Conversely, tolerogenic vaccines are largely experimental and are currently pursued in pre-clinical settings or in early-phase clinical trials and are studied based on their future potential rather than their clinical actuality. Second, classic immunogenic vaccination is based on the activation, expansion, and differentiation of memory T cell clones specific for particular infectious antigens that then provide rapid immunity to any re-exposure of that infectious pathogen. Likewise, tolerogenic vaccines are contingent upon the generation of long-lasting memory, but this memory is due to the activation, expansion, and differentiation of antigen-specific regulatory T cells that mediate antigen-specific inhibitory activity by mechanisms of active, dominant tolerance. Tolerogenic vaccines also elicit ‘passive’ tolerance marked by immunological anergy and the functional and/ or physical elimination of pathogenic T cell clones and the consequent creation of a “hole in the repertoire” marked by the passive lack of T cell reactivity to a given self antigen. Third, immunogenic vaccines usually require strong immunological adjuvants to prime the initial immunization via stimulatory interactions with innate immune receptor systems that recognize “pattern-associated molecular patterns” or PAMPs that are shared among large classes of infectious pathogens. Activation of receptor systems such as the toll-like receptors (TLR) or NOD-like receptors (NLR) on mononuclear phagocytes triggers immunogenic presentation of the associated antigens on MHC class II molecules together with strong co-stimulation to elicit activation and differentiation of naïve T cells as the founding event in the adaptive immune response. In contrast, tolerogenic vaccines are designed to have minimal adjuvant activity so that the vaccine antigens are recognized in non-activated, non-inflammatory environments that favor self-tolerance. Fourth, immunogenic vaccines in current practice are largely based on the generation of humoral immunity with an emphasis on disease prevention rather than therapy of pre-established disease. In contrast, tolerogenic vaccines must counter ongoing pathogenic T cell-mediated memory, and the emphasis is on therapy of established chronic disease rather than prevention of future disease.
Tolerogenic Vaccination for Multiple Sclerosis (MS): The Targets, the Challenges, the Strategies and the Future
The use of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as the prototypic model of MS has fundamentally shaped the core expectations and predictions of MS,1-9 including the presumption that MS is an inflammatory autoimmune disease mediated by pathogenic CD4+ T-helper cells specific for myelin proteins of the central nervous system (CNS) such as myelin basic protein (MBP), proteolipid protein (PLP), and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG). Myelin-specific CD4+ T cells may also recruit additional effector subsets with shared anti-myelin protein reactivity such as B cells and CD8+ T cells to partake in the autoimmune destruction of the CNS target tissue.10-16 The purpose here is not to debate the merits of the EAE model but rather to discuss the essential considerations inherent to this model for developing tolerogenic vaccines for MS. Many tolerogenic vaccine platforms have been tested for development in EAE and MS.17-29 These vaccine strategies for MS require consideration on three levels, including; (a) the identity and diversity of target CNS antigens, particularly the peptide epitopes of major myelin protein antigens, (b) the inherent efficiency by which these clones recognize their target self antigens, and (c) the qualitative activity of the vaccine in the midst of a pro-inflammatory local environment.
The Vaccine Target(s) in MS
‘Molecular mimicry’ is the leading model to explain the etiology of MS.30-33 This model predicts that chronic or recurring infectious agents are the etiological instigators of MS. The prediction is that such etiological agents have overlapping and partially shared antigenic epitopes with major myelin proteins. In the context of chronic or recurrent infection, these infectious pathogens are postulated to stimulate strong T cell-mediated immunity against the foreign “mimicry” epitope(s). After clonal expansion and differentiation into memory/ effector subsets, through mechanisms of immune surveillance, these crossreactive T cell clones are postulated to find and react to the endogenous crossreactive myelin epitopes in the CNS to mediate MS (Fig. 1). These infectious agents, upon repeated re-emergence from latency, may drive relapses of MS and the chronic relapsing-remitting disease course of MS.

The “molecular mimicry” model gives rise to a range of possibilities in regard to the nature of the autoantigens that drive the disease process. The key crossreactivities may be chance occurrences, and only one or two crossreactive epitopes may be responsible for initiation of the MS disease process. Conversely, the molecular mimicry may be driven by directed evolutionary pressures by which the infectious agent has adapted to a specialized infectious niche. For example, the infectious agent may be evolutionarily adapted to persist in an organ such as the CNS by bearing camouflage comprised of many epitopes that resemble and are crossreactive with the local host tissue. Mechanisms of ‘epitope spreading’ may further complicate vaccine development.34-36 “Epitope spreading” refers to a mechanism by which the instigating myelin-reactive clones drive CNS inflammation and recruit new, distinct clonotypes of naïve myelin-reactive clones into the CNS, where the latter clones differentiate into memory/ effector T cells upon recognition of a distinct set of CNS antigens to cause additional neurologic damage. Thus, over time, the anti-myelin T cell repertoire may broaden and diversify, and may acquire sufficient clonotypic diversity to sustain a chronic or progressive autoimmune course independent of any recurring infectious disease trigger.
These considerations underlie key unanswered questions that will shape the future of tolerogenic vaccine research in MS. Can effective tolerogenic vaccination be accomplished by targeting a limited number of myelin epitopes or will such vaccines need to cover a wide diversity of antigenic targets? A parallel question is the degree of patient-to-patient variability of the antigenic specificities that drive MS. The potential answers to these questions cover a wide range of possibilities, including the possibility of a common MS vaccine bearing a limited number of dominant myelin epitopes that will be effective for most MS patients. On the opposite side of the spectrum, MS vaccines may need to be individualized vaccines that cover numerous and highly diverse myelin epitopes based on unique sets of reactivities for each patient. This range of possibilities addresses important issues of feasibility and experimental approach in the design and testing of experimental vaccines. Whether pauci-clonal or broadly polyclonal T cells mediate MS is a critical consideration for tolerogenic vaccine development. If MS is mediated by T cells of restricted clonotypic diversity and little patient-to-patient variability in myelin specificities, then standard tolerogenic vaccine strategies may suffice for many MS patients. However, if MS is mediated by an ever-broadening repertoire of autoreactive T cells with substantial inter-patient variation, then new vaccine strategies will be needed to match therapy with a dynamically changing landscape of T cell autoreactivities. If the latter scenario is the case, early diagnosis and intervention will be key considerations for effective tolerogenic vaccination. New technologies will be needed to identify clonally-expanded, ‘smoking-gun’ myelin-reactive clones. Because one will not want to introduce vaccines that are off-target and not relevant to a given patient, vaccines will need to have a modular design so that epitopes can be readily added or subtracted from a vaccine cocktail to tailor the therapy to the reactivities of particular patients. Alternatively, new vaccine strategies could be developed to include full-length myelin proteins, including hydrophobic transmembrane domains. Most tolerogenic vaccine strategies have focused on defined encephalitogenic epitopes that are hydrophilic for practical reasons of solubility. Vaccines that include full length myelin proteins would need to be produced by technologies that do not result in protein aggregation, because aggregated proteins would likely cause the adverse side-effect and the strongly contraindicated production of anti-myelin autoantibodies. This spectrum of possibilities will shape the future development of optimal tolerogenic vaccines. The assumption of a common dominant MS antigen can serve as the basis to test experimental strategies designed to maximize the efficacy of tolerogenic vaccines. The assumption of myriads of vaccine targets with substantial inter-patient variation would be a compelling rationale to test novel modular vaccine designs or approaches based on full-length myelin proteins.
Antigen Recognition Efficiencies
The second consideration is the efficiency by which the myelin-reactive T cells recognize the relevant crossreactive foreign and self antigens (Fig. 1). The general consideration is that the crossreactive clonotypes recognize the foreign ‘mimicry’ epitopes of the infectious agent with qualitatively superior efficiency compared with self myelin epitopes.37-39 The differential reactivity is simply a consequence of self tolerance induction during development of the immune system, which precludes clones with strong reactivity to self.40The strength of foreign antigen recognition is considered sufficient to drive activation and the differentiation of naïve T cells into memory or effector T cells. In contrast, the less efficient myelin epitopes are postulated to lack the capacity to drive differentiation of naïve T cells. Thus, the foreign mimicry epitopes may provide the critical ‘activation energy’ to initiate autoimmune responses. The relevant myelin-reactive clones, even after achieving effector status, would continue to recognize endogenous myelin epitopes with low efficiency. Once the foreign mimicry antigen caused effector cell formation, the low efficiency recognition of myelin by effector/ memory T cells is postulated to be sufficient to elicit tissue damage39,41 but may be insufficient to sustain the immune response. Indeed, the low affinity recognition of myelin epitopes may be inherently tolerogenic.
The myelin-specific regulatory T cell networks that were overridden by the strong foreign stimulus are thought to be intact and capable of restoring homeostasis once the foreign mimicry has been cleared from the tissue (Fig. 1). These regulatory networks are most likely dominant in the absence of the infectious stimulus. The important concept is that the repertoires of the myelin-reactive regulatory T cells and the myelin-reactive conventional T cells most likely share a common myelin reactivity (representing the normal mechanism of homeostasis), but the regulatory T cells most likely do not recognize the foreign mimicry antigens due to the absence of these foreign antigens during development. If regulatory T cells per chance did crossreact with the mimicry antigens, then the immune system would not respond to these foreign mimicry epitopes, and the individual would not suffer from an autoimmune disease. Because tolerogenic vaccines contain native myelin epitopes, tolerogenic vaccination would predictably reinforce regulatory T cell function and the low efficiency interactions that promote tolerance rather than immunity, even after differentiation of the conventional myelin-reactive T cells into memory and effector subsets.
As a case in point, one of the most profoundly tolerogenic vaccines studied by our laboratory is comprised of the cytokine GM-CSF fused to the major encephalitogenic epitopes from MBP, MOG, or PLP in rat and mouse models of EAE.18,42,43 The GMCSF-neuroantigen (NAg) vaccine requires covalent linkage of the cytokine and NAg domains for tolerogenic efficacy. Conversely, a substantial number of studies have shown that GM-CSF fusions with foreign antigens act as immunogenic vaccines and can be used to augment immune responses against foreign antigens.44,45 Taken together, these studies suggest that the antigenic domain aside from the GM-CSF domain may bias the inherent activity of the vaccine. Thus, the self or nonself origins of the antigenic domain may play an important role in controlling the balance between tolerance and immunity. An important functionality of the GM-CSF domain may simply involve targeting of the vaccine to dendritic cells to promote more efficient presentation of the antigenic domain.43 The ‘self’ NAg domains of GMCSF-NAg fusion proteins, by engaging developmentally established regulatory networks, would be predicted to promote tolerance. Conversely, the ‘foreign-antigen’ domains of GMCSF-antigen fusion proteins would predominantly engage a repertoire of conventional T cells rather than regulatory T cells and thereby would drive immunogenic responses. These predictions are consistent with the experimental observations that GM-CSF may amplify the intrinsic tolerogenic or immunogenic activity of the antigenic domain. The inherent tolerogenic activity of self antigens, even in the midst of an ongoing autoimmune disease, may appear paradoxical but is a key element in the feasibility and potential success of tolerogenic vaccines.
The Environment
One of the primary concerns regarding tolerogenic vaccines is the possibility that administration of a ‘tolerogenic vaccine’ to particular patients may be immunogenic rather tolerogenic and worsen the MS disease course, as may have occurred in clinical trials of “altered peptide ligands or APL”.46 Underlying this concern is the concept that tolerogenic vaccines have tolerogenic activity because these vaccines are administered without adjuvants and thus are presented to the immune system in a quiescent, non-activated environment.47-52 The idea is that antigen presentation in the absence of costimulatory molecules and without a complement of proinflammatory cytokines is critical for inhibitory vaccine activity. However, the environment of the vaccine recipient will be difficult to control in a clinical setting because at least some patients will have inapparent infections or exposure to other pro-inflammatory stimuli either locally or systemically. If a tolerogenic vaccine is administered into such a pro-inflammatory environment, the vaccine would perhaps adversely worsen the disease course. The extent to which this issue applies to a tolerogenic vaccine platform represents a critical consideration regarding the projected success of that vaccine platform.
The notion is widely-held that a vaccine is either tolerogenic or immunogenic based on whether the vaccine is administered into a quiescent or pro-inflammatory environment. However, this idea can be challenged on theoretical and experimental grounds and may differentially apply to distinct tolerogenic vaccine platforms. Autoreactive T cells circulate in normal individuals but do not cause autoimmunity in the vast majority of persons even though the host is continually subjected to infectious disease, injury, and various inflammatory insults. Regulatory networks apparently are not so simply co-opted by inflammatory environments. Indeed, regulatory networks comprised of Foxp3+CD4+CD25+ may be strengthened by antigen recognition in the presence of B7-mediated costimulation and various cytokines, particularly IL-2.53,54 Thus, one cannot conclude that the inhibitory activity of a tolerogenic vaccine would be preempted within a pro-inflammatory environment. As a case in point, a GMCSF-NAg tolerogenic vaccine was administered at the same time and at sites immediately adjacent to the encephalitogenic peptide/ Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA) immunization. In this paradigm, GMCSF-NAg retained inhibitory activity and prevented EAE in a majority of immunized mice.18 Thus, the GMCSF-NAg vaccine retained inhibitory activity even in the midst of a CFA-polarized inflammatory environment. Thus, a critical test of a tolerogenic vaccine platform is the deliberate introduction of the vaccine in a proinflammatory environment, either administered after disease onset or together with adjuvants or other pro-inflammatory stimuli during encephalitogenic immunization. In this regard, GMCSF-NAg effectively inhibited disease when delivered into the same lymphatic drainage at the same time as the encephalitogenic/ CFA immunization. The GMCSF-NAg vaccine also inhibited EAE when given at disease onset, or alternatively, when given during established chronic EAE.18,42,43
The Future
A primary prediction of the EAE model of MS is that the study of the myelin-specific T cell repertoire of MS patients should reveal the key specificities that underlie MS. However, many studies have shown that MS patients had similar frequencies of myelin reactive T cells compared with healthy age- and gender-matched controls.55-61 The myelin-specific repertoire in MS nonetheless appears to show some evidence of clonal expansion and a more pronounced expression of an activation/memory phenotype. The ‘cause or consequence’ question however has yet to be answered, and no clear consensus has emerged regarding the diversity and inter-patient variability of the antigenic determinants that drive the MS disease process. The questions of which peptides cause pathogenesis in MS are particularly vexing. A clinical trial of an ‘altered peptide ligand’ of MBP83–99 was designed to inhibit MS but instead appeared to aggravate disease.46 This adverse effect provided suggestive evidence implicating this myelin peptide as encephalitogenic in humans. Other CNS proteins aside from the myelin antigens might be critical antigenic targets in MS,62-66 just as aquaporin-4 appears to be a major antigenic target in Neuromyelitis Optica, and the inward-rectifying KIR4.1 potassium channel appears to be a major target of the humoral immune response in many adult MS patients. Humoral responses to MOG are apparent in patients with Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis and pediatric MS. Human T cell antigen receptor chains specific for myelin peptides have been expressed in mice as transgenes together with the human MHC class II restriction alleles, and these transgenic mice show spontaneous EAE.67-69 These and other approaches provide compelling evidence that particular antigen specificities are associated with MS and related neurologic diseases. However, the true encephalitogenic drivers of MS remain unknown. As a key question for the future of the field, consideration must be given to those experimental approaches that might best reveal causal links between a given antigenic specificity and MS pathogenesis. Tolerogenic vaccines may provide the key to the solution. In this regard, a central goal of the field is to devise and test tolerogenic vaccines as interventions in MS. A major step forward would be a successful clinical trial of an efficacious tolerogenic vaccine. Such an accomplishment would verify the tolerogenic efficacy of the vaccine approach, and the identity of the vaccine NAg domain would definitively link that NAg specificity as a foundation of MS pathogenesis. Thus, clinical trials of tolerogenic vaccines may be a key experimental venue to not only treat MS but to reveal the underlying pathogenesis of MS. Thus, over the course of the next decade, the hope is that tolerogenic vaccines will begin to reveal the “nature of the beast” that is MS.



 Vitamin D is important for strong bones, teeth and immunity system. Many decades of studies have proven that Vitamin D is vital for bone and muscle growth and the regulation of other minerals in the body. Our own skin produces Vitamin D when exposed to the Sun.However, with fewer people going outside or using sunscreen and eating Vitamin D rich foods like fatty fishes (salmon, herring, tuna, sardines) and eggs, many people are feeling the effects of Vitamin D deficiency. Many health authorities suggest at least 400 IU’s per day, but others believe that is woefully inadequate and suggest up to 4,000 IU’s per day.
Vitamin D is important for strong bones, teeth and immunity system. Many decades of studies have proven that Vitamin D is vital for bone and muscle growth and the regulation of other minerals in the body. Our own skin produces Vitamin D when exposed to the Sun.However, with fewer people going outside or using sunscreen and eating Vitamin D rich foods like fatty fishes (salmon, herring, tuna, sardines) and eggs, many people are feeling the effects of Vitamin D deficiency. Many health authorities suggest at least 400 IU’s per day, but others believe that is woefully inadequate and suggest up to 4,000 IU’s per day.




